

Feel free to contact us for any feedback. Lenntech BV is not responsible for programming or calculation errors on this sheet. The constant c is equal to the amount of gas in moles, multiplied by the gas constant: These conditions are often fullfilled, for example for air at atmospheric pressure and standard temperature. This formula is called the ideal gas law.It is valid if the temperature (in kelvin) is at least 50% higher than the temperature at the critical point and the pressure does not exceed the critical pressure. This is because the molecules get more energy and move faster.Ĭ is a constant, proportional to the number of gas molecules It is widely used in the daily life particularly in European countries, though that is a non-SI unit. If the volume is constant and the temperature increases, the pressure also increases. Visit 50 Bar to Psi Conversion Bar : The bar is a unit of measurement for pressure. The pressure of a gas is related to temperature and volume. Relation between temperature, pressure and volume (ideal gas law):
If you measure the pressure in Pascal at sea-level, you will find 101325 Pa. At sea-level the pressure is also defined as 1 atmosphere, that's why 1 atmosphere equals 760 torr. It was calibrated that on sea-level the height of the mercury was 760 mm. The reason that mercury is used is that the thermal expansion of mercury is big and is mostly homogeneous. If the pressure changes, the level of the mercury in the tube changes with it. The unit of pressure used to be torr, also known as mmHG (millimeter mercury). The unit is Pascal (Pa), also known as N/m 2. Pressure ( p) is a derived quantity with its own name. Use this conversion calculator to convert American/Britis units to the metrical (SI) units.
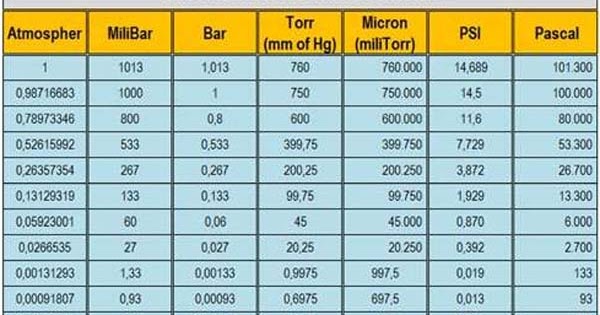
Pound-force per square inchĭefinition: A pound-force per square inch (symbol: psi) is an imperial and US customary unit of pressure based on avoirdupois units. This is true of most countries, including the United States. The kilopascal is more prevalent in scientific contexts such as material science, engineering, and geophysics. Exceptions include certain countries that use either the imperial or United States customary systems of measurement, such as the United States, in which the unit of pound per square inch is more commonly used. In 1971, at the 14 th General Conference on Weights and Measures, the pascal was adopted as an SI derived unit of pressure.Ĭurrent use: The kilopascal is widely used worldwide in countries that have adopted SI. The kilopascal is simply a multiple of the pascal, as is common within SI. History/origin: The unit, pascal, is named after Blaise Pascal, a French mathematician and physicist. A kilopascal is defined as 1,000 Pa, where 1 Pa is defined as the pressure exerted by a 1 newton force applied perpendicularly to an area of one square meter, expressed as 1 N/m 2 or 1 kg/m Definition: A kilopascal (symbol: kPa) is a multiple of the pascal (Pa), an SI (International System of Units) derived unit of pressure used to measure internal pressure, Young's modulus, stress, and ultimate tensile strength.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
